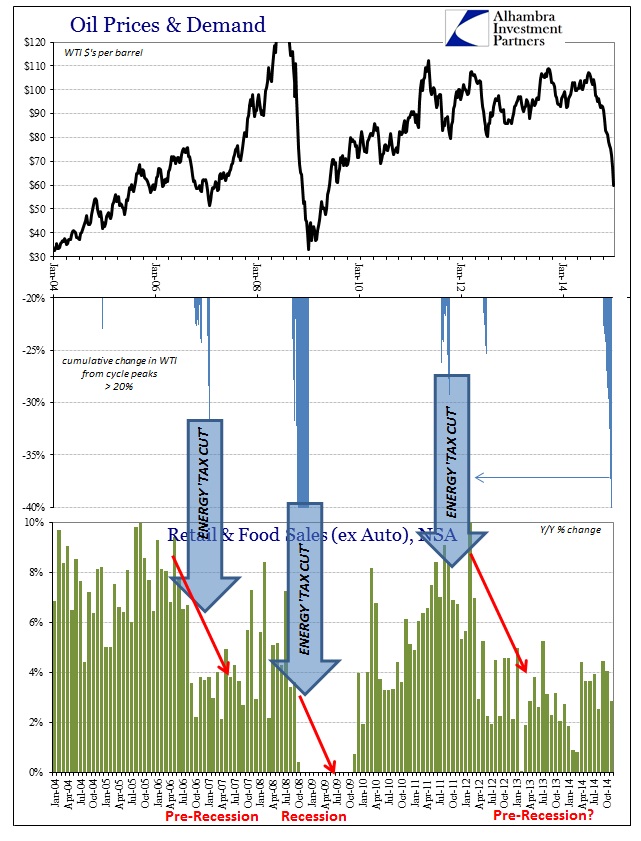
As recent oil news make headlines we have decided to take a closer look at the OIL price and provide a perspective in considerations of few significant industry and geopolitical trends.
Fossil oil is and will
play a significant role in satisfying global energy demand. The medium to
long-term trend is determined by multiple factors such as among others: the
status of the global economy, geopolitical events, technological advances as
well as consumer choices. The two main variables impacting supply and demand
have been on the one hand a significant increase in the energy demands of
developing countries, and on the other hand the emerging of a wider variety of
energy supply typologies (i.e. oil sands, fracking technology) altering the
traditional energy supply routes and therefore also geopolitical choices.
1.
OVERVIEW OF THE OIL SUPPLY AND DEMAND
In 2013 crude oil global
consumption grew around 1.3 million b/d (+1.4%), with an average of 90.4
million for year. The Energy Information Administration forecasts an increase
of 1.1 million b/d in 2014 and 1.4 million b/d in 2015.
In the
medium-term period (2012-2018) Reference Case Demand could increase by an
annual average of 0.9 mb/d, reaching 94.4 million b/d in 2018. Europe, Asia and
Russian demands are rising very slowly, as illustrated in Table 1 while developing
countries demand rise faster, with an increase of 1.1 mb/d every year.
The outlook
for the second half of 2014 shows that the oil demand of non OECD countries
will be higher compared to the OECD countries.
Table 1 Medium-term oil demand
outlook in the Reference Case
Source:
World Oil Outlook 2013
In the long-term
period (2012-2035) Reference Case Demand could reach an increment of 20 mb/d
each year, this value could rise up to 180,5 mb/d in 2035. The biggest share of
this forecasted increase should come from developing countries.
Table 2 World oil demand outlook in the Reference Case
Source:
World Oil Outlook 2013
Oil and other liquid combustibles
global supply is estimated to grow 1.5 mb/d in 2014 and will decrease to 0.9
mb/d in 2015. Nevertheless, Non-Opec countries supply presents an estimated
upward trend, with forecasts assessed at around 1.8 mb/d in 2014 and 1.1 mb/d
in 2015.
Figure 1 Change in non-OPEC
supply, 2012–2018
Source: World Oil Outlook
2013
In the
medium-term 2012-2018, as illustrated in Figure 1, total non-Opec supply is expected
to constantly rise by 5.7 mb/d. The two main variables impacting these
estimates are the supply of “tight oil” and “oil sands”.
These could create
additional supply, in particular in Latin America (Brazil and Colombia), in
Middle East and Africa, even if in those countries supply may be negatively affected
by political instability.
EIA’s data
show that crude oil Opec production had an average of 29.9 mb/d in 2013, with a
decrease of 1 million with the respect to the year before, due to the oil
production outage in Libya, Nigeria and Iraq. This decrease is partially mitigated
by a strong growth in non-OPEC country supply.
The EIA
outlook indicates that Opec production should decrease of 0.3 mb/d in 2014 and by
other 0.2 mb/d in 2015.
In fact, 8
of 12 Opec members, present a negative production in 2013, such as Libya. The other
4 countries try to maintain a stable production, furthermore, Iraq increase its
production from 1.75 mb/d to 3.25 mb/d starting from 2005 to 2013. OPEC
conservative production allowed to preserve oil price around 100-110 dollars
per barrel during the last few years.
The graphic
below, reported by Kent Moors, Phd, in Money Morning, shows that demand will
continue to grow until 2025, while supply instead is expected to decline. Based
upon these estimates it is possible to experience a shortfall between demand and supply.
Figure 2 World oil demand
and supply
Source: Money Morning 2014
2.
FORECASTING OIL PRICES
Lately crude
oil forecasts depend heavily on the oil exporters geopolitical uncertainty. The
reduced risk to Iraqi oil exports and the news regarding increasing Libyan oil
exports contributed to a drop in the Brent crude oil spot price to an average
of $107 per barrel in July2014, $5/bbl lower than the June average, as reported
in EIA outlook of August 2014.
The Saudi
active intervention in price setting over the past few weeks, coupled with
further signs of a weakening of the Chinese economy have both contributed to
driving the price to a 4 years low ($80 USD/bbl). Some add that there may be
geopolitical interests at play to further weaken Russia by virtue of keeping
the price of oil particularly low. Regardless of the geo-political reasons
behind this short term oil price low, it is reasonable to expect a medium term
increase to a more reasonable price level, especially if the US economy
confirms its acceleration as indicated by the latest indicators released by the
Federal Reserve.
Based upon
recent events oil price forecasts are highly uncertain, and the current values
of futures and options contracts suggest that prices could differ significantly
from the forecasted levels. Implied volatility averaged 16 %, establishing the
lower and upper limits of the 95% confidence interval for the market's
expectations of monthly average WTI prices in November 2014 at $84/bbl and
$111/bbl, respectively. Last year at this time, WTI for November 2013 delivery
averaged $103/bbl and implied volatility averaged 21%. The corresponding lower
and upper limits of the 95%confidence interval were $85/bbl and $125/bbl.
Figure 3 Uncertain oil
prices are expected to fall
Source: IMF 2014
According to
World Oil Outlook (2013), the nominal OPEC Reference Basket price will
be remain on an average of $110/bbl until 2020, and then it will increase in
both real and nominal terms.
In nominal terms,
we suppose that the nominal price will reach $160/bbl within 2035, whereas in
real terms it will reach $100/bbl. It represents a slight shift upward than WOO
2012 expected.
Table 3 OPEC Reference
Basket price assumptions in the Reference Case
Source: World Oil Outlook 2013
3.
CONCLUSIONS
Eventually,
oil price is set to rise, influenced by fear and uncertainty from Middle Eastern
and North African countries. The new geopolitical instability of the late 2014,
continued nowadays in Iraq and in all Middle East, causes oil production shortages
that could take oil price back up to $110-120/bbl.
We judge the
existing low price as temporary and due to the following conjunction of few
geopolitical and economic events: a slow down in Chinese manufacturing output,
Saudi oil discounting IS heavily discounted although limited supply. We
acknowledge the above as short-term temporary factors.
Although we
expect oil prices to rise in the long-term (2014-2035) we forecast that any
sustained price above $150 USD maintained for a long period of time is going to
accelerate the oil for gas substitution trend. We therefore believe that the
probability of high OIL prices for a sustained period of time is be quite low.
Oil price is
closely connected to the futures market, that forecasts an increase oil price
and it is minor influenced by the production.
As political
instability grows in key oil producing areas and extraction technology
progresses, oil companies have more incentives to explore and extract oil in
international waters away from conflict areas. Thanks to new technologies these
new offshore areas are now within reach.
REFERENCES
EIA, Short-Term
Energy Outlook August 2014, Energy Information Administration, U.S. Department
of Energy: Washington, DC.
Kent Moors, Money
Morning, August 2014
IMF (2014),
Regional Economic Outlook. Update: Middle East and Central Asia Department,
International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC.
OPEC (2013), World
Oil Outlook, Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, Publications:
Vienna.
Authors: Marta Pezzoni & Luca Gorlero